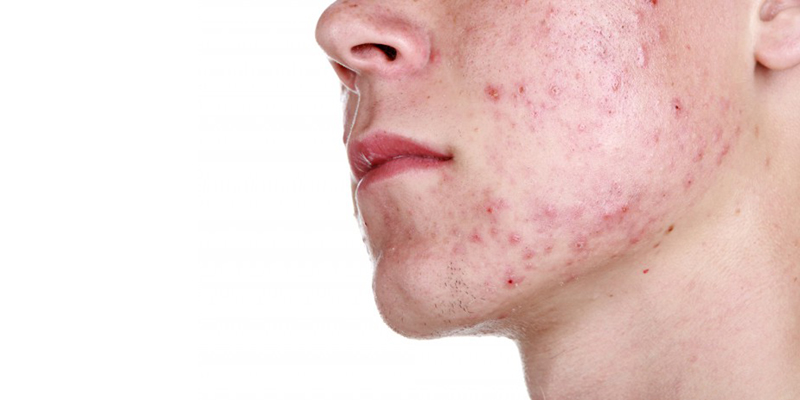
Acne
Acne
The importance of early management of ACNE cannot be overstated. Once ACNE sets in and damage to skin occurs, complete recovery may be difficult to attain. Best results for prevention and longevity is early detection of a possible problem combined with conventional treatments, nutritional supplements and a healthy diet and lifestyle.
Mild acne can be treated with the ZO SKIN HEALTH skin care range which is available at Clínica Privé. For mild acne a consultation is not necessary and the skin care range may be purchased.
If you suffer from moderate to severe acne (many lesions) a consultation is mandatory for a customized treatment package to be designed for your condition.
What is Acne?
Acne (acne vulgaris) is a dermatologic condition which affects approximately 80-95% of adolescents as their bodies go through puberty, but luckily its occurrence declines over the following years until middle age. This condition is characterized by lesions that most often appear on the face and neck, but it is not uncommon to develop these lesions on the chest, back, shoulders and upper arms too. Acne vulgaris, the most common skin disorder, affects virtually all individuals at least once. Incidence peaks in 18-year-olds, but substantial numbers of 20- to 40-year age group also develop the disease.
Adolescent boys and young men are more likely to have acne than their female counterparts and make up the majority of severe scarring cases, due to the fact that acne is triggered by androgens (male hormone) fluctuations.
Women are more likely to suffer from ongoing acne that commences or reappears during their early adult years. Around 8% of women have acne persisting into their 30’s and in some it continues into their 40's and occasionally 50's. Why this occurs is poorly understood but may be related to hormones, childbirth, menopause, or stopping the pill. Adult women may be treated at the period and at ovulation when acne is especially severe, or throughout the entire cycle.
There is also a subset of women with “true” hormonal acne who have abnormal levels of androgenic (male-type) hormones. These women often have accompanying excess facial hair (also hormonally regulated) and irregular menstrual cycles, although women who have normal hormone levels may also have excess hair. The sebaceous glands of patients with acne are likely to be hypersensitive to androgens (male-type) hormones.
What are the important psychological aspects of acne?
The effects of acne should not be underestimated. It can persist for years; produce disfigurement and permanent scarring; and have significant psycho-social consequences, including diminished self-esteem, embarrassment, social withdrawal, depression, anxiety and unemployment. The extent and severity of these effects underline the importance of providing adequate therapy, such as the ZO SKIN HEALTH range which produces more than 80% improvement in 8 weeks in mild to moderate cases.
How does acne form?
Acne is characterized by the formation of comedones (blackheads), pimples, cysts and abscesses (in worst cases). These lesions are formed on the skin when the pores in the skin are blocked. This blockage causes oil to be trapped, together with dead skin and bacteria within the hair follicles. In normal circumstances, the sebaceous glands (which have the function of secreting an oily substance called sebum) are attached to the hair follicles and allows the sebum to travel up the hair follicle and onto the skin. However, if there is a blockage in the hair follicle, the sebum can't get out, and this can sometimes cause the formation of a blackhead (comedones). Blackheads are the result of the blocked oil that oxidizes, causing further inflammation and an influx of white blood cells.
Meanwhile, normally present bacteria (Propionibacterium acnes) begin to break down the trapped sebum within the hair follicle. The subsequent result is further and aggravated inflammation, as white blood cells attack the bacteria. Pus forms within the lesion causing the lesion to enter the whitehead stage. In more severe stages with severe inflammation and infection, an abscess - a painful pus-filled pocket within the skin - may form.
What is the Pathogenesis of acne: A Summary?
Acne arises from the interaction of 4 factors:
1. Dead skin cells blocking the oil duct results in Comedogenesis. The first sign of altered keratinization is a blackhead which consists of keratinized material and lipid material. This Abnormal Keratinization results in formation of keratin plugs which blocks off the drainage of the sebaceous follicles, leading to accumulation of inflammatory debris and increased bacterial numbers of P acnes.
2. Too much oil production caused by androgenic hormonal stimulation of sebaceous glands at puberty or later (hormonal triggers).
3. Too many bacteria: Proliferation of P acnes in this blocked follicle.
4. Too much Inflammation: is a direct or indirect result of P acnes proliferation. Rupture of the inflammatory follicle onto the skin results in the redness around the acne lesion. Extension of inflammation into the skin results in formation of the inflammatory lesions of acne, which include papules, pustules, and nodules. The result is redness and pus.
What are additional causes that have been associated with the development of acne?
- Hormones; In both men and women, the androgen hormones are present in much higher concentrations at puberty and acne results. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) leads to higher levels of male hormones which can cause acne in female patients.
- Genetic factors (family members have bad acne)
- Flare Factors for acne are: stress and depression, menses and puberty (new onset hormones).
- Environmental factors such as high humidity causing swelling of the skin.
- Diet: a poor, unhealthy diet high in saturated fats, MSG's and preservatives can aggravate acne in someone who is allready prone to this condition.
- Cosmetics especially certain moisturizers and foundations.
What skin care ingredients must one AVOID if you have acne?
- Cinnamon oil,
- Cocoa butter,
- Cocus nucifera,
- Isoprpopyl isostearate,
- Isopropyl myristate,
- Isopropyl myristate,
- Butyl stearate,
- Isostearyl neopentanoate,
- Myristyl myristate,
- Octyl palmitate,
- Isocetyl srearate,
- Propylene glycol 2,
- Myristyl propionate,
- Lanolin,
- Peppermint oil,
- Decyl oleate, and
- Octyl stearate.
How can acne be classified?
Acne can be classified as mild, moderate or severe inflammatory acne and is based on lesion count and whether nodules are present, or not.
- Mild to moderate acne has papules, pustules and comedones, without any nodules present in the skin.
- Severe acne has many papules, pustules, comedones and/or more than 5 nodules present in the skin. Cysts may also be present in these severe cases.
Severe acne may be more common in males and this kind of acne should be evaluated as scarring is inevitable.
What are the types of Acne lesions?
- Open comedones (blackheads): These lesions are very common and consist of dilated pores and/or hair follicles, that are filled with a combination of sebum, dead skin cells and bacteria. This mixture gets trapped within the follicle creating a central, dark and solid plug. The follicles are not completely blocked, and it appears black because of oxidation of the trapped mixture, not dirt.
- Closed comedones (whiteheads): These form when the dead skin cells and sebum completely block the opening of a hair follicle, usually following after a blackhead has formed.
- Pustules: This whitehead type of lesions is pus-filled and inflamed. Once these lesions rupture into the skin, they form pustular heads.
- Papules: This type of whitehead (5 mm or less) is a type of lesions that has become swollen, red and inflamed.
- Nodules: This type of lesions is a solid, dome- or irregularly shaped, inflamed lesions that extend deep into the skin. If left untreated these lesions can cause tissue damage and scarring because it affects deeper skin layers too. This type of nodular acne is the most severe form of the condition and can be very painful, even without touch.
- Cysts: These sac-like lesions contain a liquid, or semi-liquid, substance that is made up of white blood cells, bacteria and dead skin cells. Left untreated they can result in scarring, and may be very painful and severely inflamed. When an individual has the formation of cysts and nodules together it is called nodulocystic acne, which is also very severe and requires medical treatment.
What are the causes of Acne?
Acne can be caused by both environmental and genetic factors, but genetics seems to the predominate cause of the condition in most individuals. It was found in one large twin study that 81% of disease variance (that is, the difference from what would normally be expected) was attributed to genetic effects, and the remaining 19% to environmental factors. Furthermore the study also showed that if an individual has a family history of acne it significantly increased personal risk of developing the condition.
Puberty is the stage in a person’s life when there is an increase in the production of the male hormone testosterone (in both men & woman) which leads to the enlargement of the sebaceous glands in the skin and creates a contributing factor to acne formation. If the sebaceous glands are enlarged they produce more sebum, which leads to the aforementioned plug formation, and this then creates a fertile environment in which bacteria can grow and multiply.
Unlike male-hormones (androgens), female-hormones (estrogens) have a beneficial effect on acne, this is then why some doctors recommend the use of birth control pills for women who have acne. However, when a woman's estrogen levels decline acne may worsen (this drop in the hormone levels happen each month just before the menstrual cycle begins).
Acne or acne-like lesions can also develop in response to various substances, including corticosteroids, lithium, and some psychotropic drugs. There are also other environmental causes such as exposure to tobacco smoke, coal tar derivatives and industrial oils which need to be steered clear of. Substances to also avoid include oils in aerosol sprays, as well as excessive washing or scrubbing of the skin. Over washing can aggravate acne because it causes increased skin-oil production leading to more acne formation. There are types of cosmetics, oil-based hair products, and suntan lotions which can block oil glands and worsen acne so they are best avoided. It is better to use hypoallergenic, oil-free and water-based products that do not clog pores. It is interesting to note that, despite popular opinion, the conventional medical view is that acne is not caused by poor hygiene or by eating specific foods, such as chocolate, pizza, and soda although the evidence is mixed.
What are the In-Office treatments available at Clínica Privé to treat and improve the post healing acne scarring?
- HydraFacial MD / Microdermabrasion gently polishes the skin. Can be used for mild acne, where the lesions are not currently active.
- ZO Medical Grade Facial are cleansing facials which are prescribed once a month to remove pustules and comedones so as to facilitate healing of the acne condition with as little damage to the skin as possible.
- An Extraction Peel is a Beta Salicylic acid peel combined with a Deep Cleanse Facial and Laser Genesis.
- At Clínica Privé we offer the following peels for our acne patients: Beta Salicylic acid peel, Azelan, Modified Jessners Peel and TCA peels for our acne patients depending on Skin Type, severity and budget.
- Vbeam Laser Healing Program.
- The Laser Genesis procedure, a 5 in one treatment, reduces the size of the sebaceous gland, reduces inflammation in the papule and nodule, reduces pore size, improves acne scarring and pigmentation.
- 10 or 15% TCA Peel overlays to the affected areas improves the active acne lesion as well as improving PIH and acne scarring.
- LED Light Therapy uses red and blue light therapy, plus a salicylic acid silk peel to improve acne by destroying bacteria and reducing inflammation in the acne lesion.
Standalone PDT/ LED treatment alternating with the red and the blue light every 48 hours. 8 treatments would be needed to improve acne.
The blue light kills the acne bacteria.
The red light is anti inflammatory.
- Carboxytherapy around acne lesions, or into acne scars, reduces the acne lesion and improves the acne scarring.
What are the goals of successful acne topical treatments such as ACNETROL?
The goals of acne treatment are to:
- lessen physical discomfort from inflamed acne lesions
- improve appearance
- prevent or minimize potential adverse psychological effects
- minimize any scarring
- treating lesions and preventing new lesions from developing.
Topical treatment – ZO SKIN HEALTH skin range is indicated for patients with non-inflammatory comedones or mild to moderate inflammatory acne. Medications used in topical treatment may act primarily against comedones (comedolytic agents) or inflammatory lesions (antibacterial agents and antibiotics). A principal goal of therapy should be reduction or elimination of the precursor of all acne lesions— microcomedones.
Prescription Acne Medication Include:
- Topical Antibiotics
- Topical Retinoids
- Oral Antibiotics
- Oral Hormonal Medications
- Accutane
How does one prevent acne?
- Avoid the sun as overexposure to the sun can worsen acne, and cause post inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) of inflamed lesions.
- Use cosmetics sparingly. Use only hypoallergenic, breathable cosmetics.
- Wash face gently in the mornings and at night with unscented, oil-free cleansers and keep the skin clean. It is important to remember: Acne is not caused by dirt. Avoid scrubbing inflamed skin as this will make acne worse and spread the infection to larger parts of the skin.
- Resist the urge to squeeze, scratch or pick at acne lesions. Let them drain when they are ready. Causing trauma to the skin will result in potential scarring and worsening of the condition as infection spreads.
- Young men who suffer from moderate to severe acne should use a new razor blade every time they shave to lessen risk of infection.
- It is important that men avoid alcohol-based aftershaves. If possible, use herbal alternatives that include essential oils of lavender, chamomile, or tea tree oil to sooth the skin.
- Eliminate foods which are high in fat, hormones, and iodine.
- Ensure your diet consist of a wide range of whole, natural foods, especially raw foods. Avoid processed foods with additives and trans-fatty acids.
- Drink adequate liquids, especially pure water and green tea, which helps to flush your system and keep the skin hydrated.